AI & APIs
Artificial intelligence technologies and concepts relevant to API documentation. This section covers AI tools, terminology, and practices that impact how technical writers create and enhance API documentation.
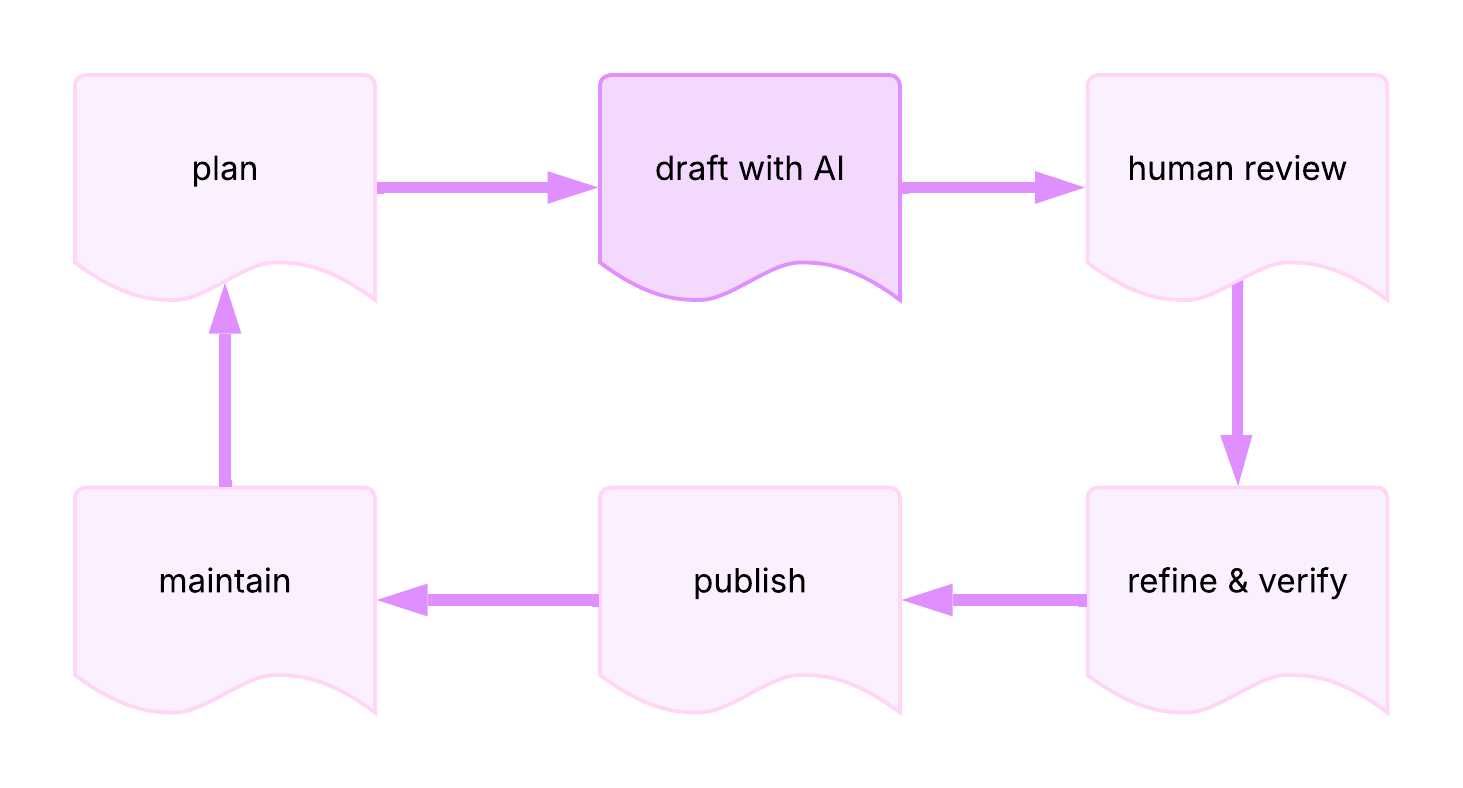
AI-assisted documentation workflow:
AI
Definition: acronym for Artificial Intelligence; technologies that use computers and large datasets to perform tasks, make predictions, or solve problems that typically require human intelligence
Purpose: encompasses tools and techniques increasingly used in API documentation workflows, from content generation to automated testing
Related Terms: AI agent, genAI, Large Language Model, Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing, prompt engineering
Sources:
- University of Washington: "AI + Teaching"
- UW API Docs: Module 1, Lesson 4, "Intro to AI and API docs"
AI agent
Definition: single implementation and/or instance of an autonomous system that independently plans, uses tools, and takes actions to accomplish tasks on behalf of users; combines NLP - Natural Language Processing - with reasoning capabilities to break down complex goals into steps, gather information through external tools, and adapt its approach based on observations
Purpose: enables automation of complex, multi-step workflows that previously required human decision-making; particularly valuable in API documentation contexts for automating docs testing, generating code examples, maintaining accuracy across docs updates, and integrating with external systems through APIs and tools
How AI Agents Work: agents operate through a cycle of reasoning about the task, deciding which actions or tools to use, observing results from those actions, and adapting their plan accordingly; they maintain memory of past interactions, can call external APIs or tools, and continue iterating until the goal is accomplished or they determine they cannot proceed
agentic AI vs AI agent skills
Also known as compound AI systems, agentic AI refers to the broader field and architectural pattern of building autonomous AI systems; similar to how "a microservice" is an instance while "microservices architecture" is the pattern.
AI agent skills refer to modular folders of instructions, scripts, and resources that AI agents can discover and load on demand. Instead of hardcoding knowledge into prompts or creating specialized tools for every task, skills provide a flexible way to extend agent capabilities.
Note: agentic AI is an emerging technology; humans must build sophisticated mental models to enable agents to develop the correct intuition to make effective, positive changes in software systems
Example: tech writer → Docs Detective → Claude Code skills workflow -
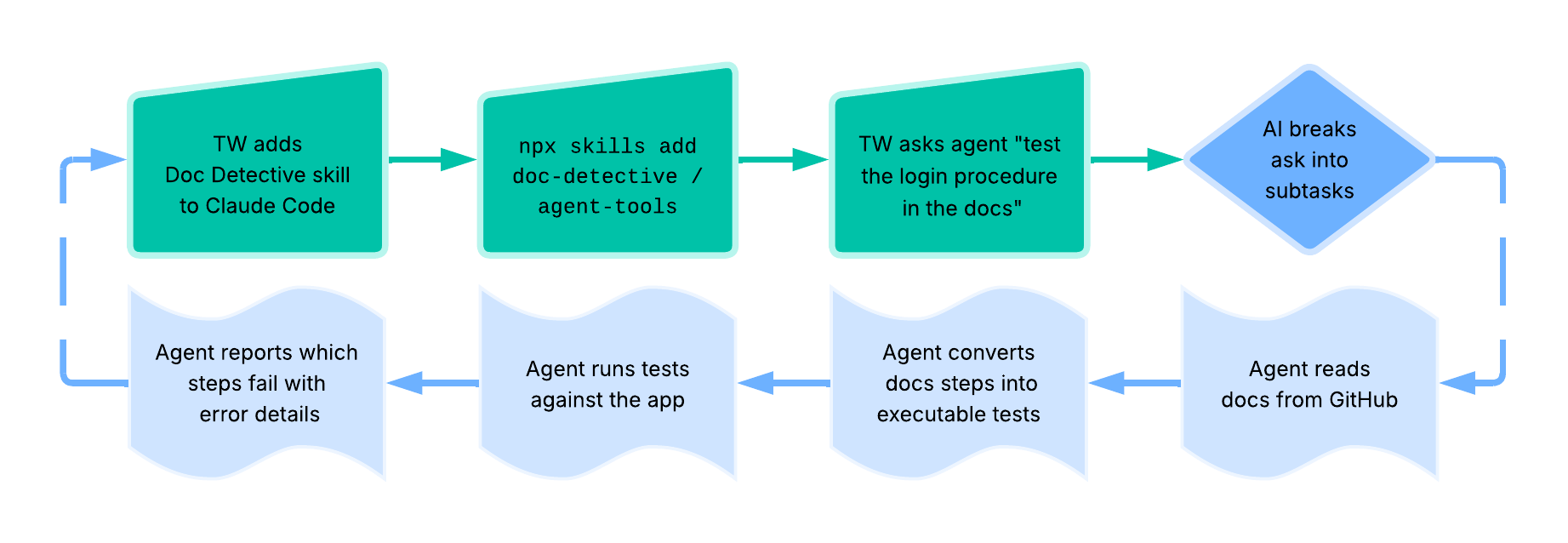
Related Terms: AI, API documentation testing, docs-as-tests, Large Language Model, MCP server, Natural Language Processing, prompt engineering, RAG
Sources:
- IBM: "What Are AI Agents?" by Anna Gutowska
- Stripe: "Minions: Stripe's one-shot, end-to-end coding agents" by Alistair Gray
- GitHub: doc-detective/agent-tools
- Google Cloud: "What is agentic AI?"
- Spring by VMware Tanzu: "Spring AI Agentic Patterns (Part 1): Agent Skills - Modular, Reusable Capabilities" by Christian Tzolov
- Wikipedia: "AI agent"
AI-assisted documentation
Definition: documentation created or enhanced using AI tools while maintaining human oversight for accuracy, technical correctness, and quality
Purpose: accelerates documentation workflows by handling repetitive tasks, allowing technical writers to focus on complex explanations, accuracy verification, and user experience
Example: using AI to generate initial drafts of API reference descriptions, then manually reviewing and enhancing with technical details and examples
Related Terms: AI, genAI, Large Language Model, Mintlify
Source: UW API Docs: Module 1, Lesson 4, "Intro to AI and API docs"
AI-assisted usability analysis
Definition: use of AI tools to analyze usability test results and identify patterns in user behavior or interface issues
Purpose: accelerates analysis of certain types of usability data while recognizing the limitations of AI in evaluating human factors
Appropriate use cases:
- Mechanical tests: language clarity, navigation patterns, consistency checks
- Pattern identification: recurring user errors, common interaction sequences
- Quantitative analysis: time-on-task, completion rates, click paths
Limitations:
- Can't reliably assess human factors: credibility, perception, satisfaction, emotional responses
- AI capabilities and best practices evolve rapidly, requiring ongoing evaluation
- Results should supplement, not replace, human expertise in usability research
- Interpretation quality depends on the specific AI tools and prompts used
Note: this represents current perspectives on AI implementation into usability testing strategies and may evolve as AI capabilities develop
Related Terms: AI, guerrilla usability testing, usability testing
Source: UW API Docs: Module 4, Lesson 3, "Review usability testing for API"
AI bias
Definition: systematic errors or unfair outcomes in AI systems that reflect prejudices present in training data or model design
Purpose: awareness of AI bias ensures documentation teams critically assess AI-generated content rather than accepting it as authoritative, particularly for examples involving people, places, or cultural contexts
Related Terms: AI, training data
Sources:
- University of Washington: "AI + Teaching"
- UW API Docs: Module 1, Lesson 4, "Intro to AI and API docs"
genAI
Definition: acronym for Generative AI; AI systems that create new content by identifying patterns in training data and using probability to generate text, images, or other media
Purpose: assists API documentation writers with drafting, editing, and formatting tasks while requiring human oversight for accuracy and quality
Example: using Claude or ChatGPT to draft initial API endpoint descriptions that writers then refine and verify
Related Terms: AI, Large Language Model, Machine Learning, prompt engineering
Sources:
- University of Washington: "AI + Teaching"
- UW API Docs: Module 1, Lesson 4, "Intro to AI and API docs"
knowledge graph
Definition: also known as a KG; structured representation of knowledge using entities - concepts, objects, events - and the relationships between them, organized in a graph format that both humans and machines can query and reason about
Purpose: enables semantic understanding and intelligent querying of API documentation by representing relationships between endpoints, parameters, authentication methods, error codes, and other API concepts; supports AI-powered documentation search, chatbots, and automated content assembly
Example: a KG enables AI to traverse relationships to
answer development questions such as "What authentication does the payment
endpoint need?" - instead of relying on keyboard matching in documentation
text, the KG reveals that the payment endpoint is protected by
"OAuth 2.0", which requires client credentials -
client_id, client_secret, and scope - and generates a bearer token
used in requests
Interactive KG Explorer
OAuth 2.0
Related Terms: content, diagram, information architecture, liquid content, modular content, ontology, RAG, structured content
Sources:
Large Language Model
Definition: also known as an LLM; form of genAI trained on large amounts of text that generates human-like responses using deep learning and neural networks
Purpose: handles repetitive or foundational documentation tasks such as generating boilerplate descriptions, summarizing content, or translating text
Example: LLMs can draft initial OpenAPI specification descriptions or generate code examples in many programming languages
Related Terms: AI, AI agent, genAI, liquid content, Natural Language Processing, prompt engineering, RAG
Sources:
- University of Washington: "AI + Teaching"
- UW API Docs: Module 1, Lesson 4, "Intro to AI and API docs"
liquid content
Definition: content strategy that uses AI to transform and personalize kinetic content; content that adapts in real-time based on user context, preferences, or behavior, typically powered by LLMs to transform between formats - text, audio, video, summaries - while maintaining accuracy
Purpose: delivers personalized documentation experiences and enables content to flow across different formats and interfaces based on user needs; represents the AI-powered implementation of kinetic content principles where LLMs actively reshape content for different consumption modes
Why this belongs in AI & APIs: liquid content is directly tied to AI
capabilities, has specific emerging use cases in publishing, and sits at
the technical intersection of AI and content delivery, while other content
strategies may or may not be AI-assisted
Example: liquid content transformation paths -
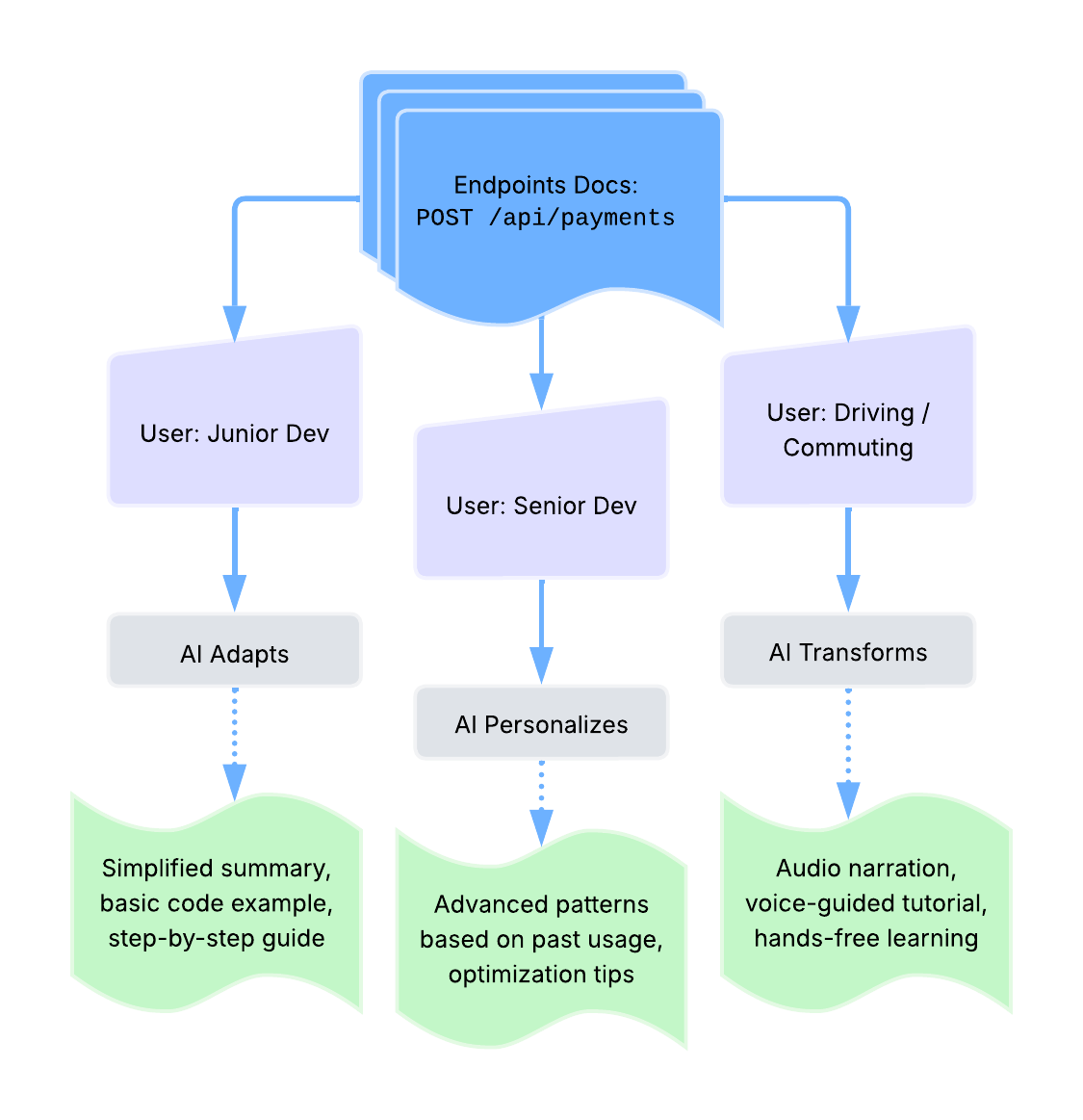
Related Terms: content, kinetic content, Large Language Model, modular content, real-time, structured content
Sources:
- Digiday Media: "WTF is liquid content?" by Sara Guaglione
- Reuters Institute: "Journalism, Media and Technology Trends and Predictions 2026" by Nic Newman
- Story Needle: "Are LLMs making content 'liquid'?" by Michael Andrews
Machine Learning
Definition: practice of using algorithms and large datasets to train computers to recognize patterns and apply learned patterns to complete new tasks
Purpose: enables AI tools to improve API documentation through pattern recognition in existing documentation, automated categorization, and predictive suggestions
Related Terms: AI, genAI, Natural Language Processing
Sources:
- University of Washington: "AI + Teaching"
- UW API Docs - Module 1, Lesson 4, "Intro to AI and API docs"
MCP server
Definition: acronym for Model Context Protocol server; a server implementation that enables AI assistants to programmatically access external tools, data sources, and services through a standardized protocol; acts as a bridge between AI models and the resources they need to complete tasks
Purpose: provides a standardized way for AI assistants to interact with tools and data that exist outside their training data; enables technical writers to build workflows where AI can access internal documentation systems, retrieve files from cloud storage, search knowledge bases, or execute commands—all through a consistent API-like interface; particularly relevant for documentation teams looking to integrate AI assistance into their existing toolchains without rebuilding infrastructure
How MCP Servers Work:
- MCP servers expose resources like files, database records, or API endpoints, and tools like search functions, file operations, or commands, through a JSON-RPC interface
- AI assistants connect to MCP servers as clients, sending requests to access resources or invoke tools
- the protocol handles authentication, authorization, and data exchange between the AI and external systems
- multiple MCP servers can run simultaneously, each providing access to different tools or data sources
Example: updating an API changelog using MCP servers
Common Use Cases for Technical Writers:
- searching internal documentation systems - Confluence, SharePoint, Google Drive
- fetching API specifications from version control - GitHub, GitLab
- accessing customer support data to identify documentation gaps
- automating repetitive documentation tasks across multiple platforms
- integrating AI assistance with existing docs-as-code workflows
Related Terms: AI agent, authentication, JSON, JSON-RPC, REST API, webhook API
Sources:
- GitHub Repository, Anthropic: "Model Context Protocol servers"
- LF Projects, LLC.: "What is the Model Context Protocol (MCP)?"
Natural Language Processing
Definition: also known as NLP; computer's ability to analyze and generate responses that mimic human language use through machine learning on large text datasets
Purpose: powers features in documentation tools such as search capability, autocomplete, spell-check, and automated translation of API documentation
Example: NLP enables smart search in API documentation that understands queries like "how to authenticate" and returns relevant authentication endpoints
Related Terms: AI, AI agent, Large Language Model, Machine Learning
Sources:
- University of Washington: "AI + Teaching"
- UW API Docs: Module 1, Lesson 4, "Intro to AI and API docs"
prompt engineering
Definition: practice of crafting effective instructions and queries to AI systems to generate desired outputs
Purpose: enables documentation teams to consistently collect useful results from AI tools by providing clear context, constraints, and expected output formats
Example: requesting "Generate an OpenAPI description for a
GET endpoint that retrieves user profiles, including response codes
and example JSON" rather than "describe this endpoint"
Related Terms: AI, AI agent, genAI, Large Language Model
Sources:
- University of Washington: "AI + Teaching"
- UW API Docs: Module 1, Lesson 4, "Intro to AI and API docs"
RAG
Definition: acronym for Retrieval-Augmented Generation; AI technique that combines information retrieval with text generation to produce accurate, contextually relevant answers to technical questions; retrieves relevant docs and/or data from a knowledge base, then uses that context to generate responses rather than relying solely on the AI model's training data
Purpose: improves accuracy and reduces hallucinations in AI-powered docs tools by grounding responses in real source material; enables AI assistants to provide up-to-date, domain-specific answers with verifiable sources
RAG vs GraphRAG: GraphRAG is an implementation approach that uses knowledge graph structures to improve retrieval quality, but the fundamental concept of grounding AI responses in source material remains the same
Example: when a developer asks "How do I authenticate?", a RAG-based system fetches relevant sections from authentication docs, API reference, and code examples, then generates a synthesized answer such as "Based on the authentication guide, you need to include your API key in the Authorization header as a Bearer token" with citations to the source docs
Related Terms: AI agent, docs-as-ecosystem, domain knowledge, Fin, Inkeep, Kapa.ai, knowledge graph, Large Language Model
Sources:
- Amazon Web Services, Inc.: "What is RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)?
- GeeksforGeeks: "What is Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)?
- IBM: "What is GraphRAG?"
- Wikipedia: "Retrieval-augmented generation"
training data
Definition: large datasets used to teach machine learning models to recognize patterns and generate responses
Purpose: understanding training data limitations helps documentation teams recognize when AI outputs may contain biases, outdated information, or inaccuracies requiring verification
Related Terms: AI, genAI, Large Language Model, Machine Learning
Sources:
- University of Washington: "AI + Teaching"
- UW API Docs: Module 1, Lesson 4, "Intro to AI and API docs"