Workflows & Methodologies
Development and documentation workflows for API projects. This section covers methodologies, testing approaches, and lifecycle management practices that guide how API documentation teams plan, create, test, and maintain their work.
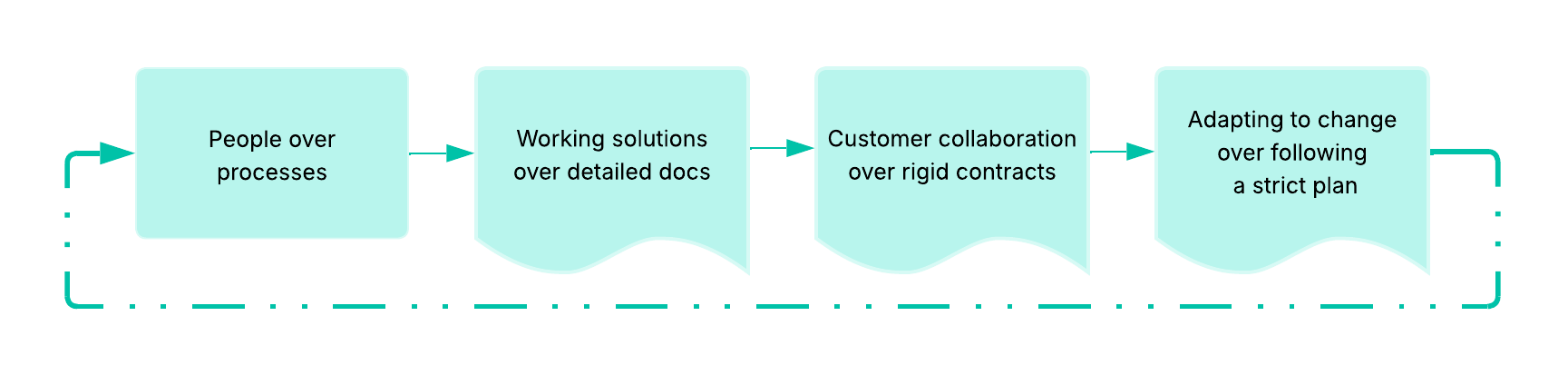
Agile
Definition: methodology with a collection of project management frameworks that break projects down into smaller phases and rely on iterative cycles
Purpose: allows teams to adapt to changes and regularly refine their work through flexibility rather than linear, rigid planning
Example: key values -
Related Terms: CI/CD pipeline, docs-as-code, docs-as-ecosystem, docs-as-tests, Document Development Life Cycle, project management methodology, Scrum, Waterfall
Sources:
- "Manifesto for Agile Software Development"
- UW API Docs: Module 2, Lesson 3, "Introduction to Project Scheduling"
- Wrike: "What Is Agile Methodology in Project Management?" by Artem Gurnov
API documentation testing
Definition: the practice of validating that APIs function correctly, return expected responses, handle errors appropriately, and meet performance requirements
Purpose: ensures API reliability and accuracy before production deployment; in API documentation contexts, validates that documented endpoints, parameters, and code examples work as written; catches breaking changes that would make documentation inaccurate or misleading to developers
Why this belongs in Workflows & Methodologies: describes a testing
practice and validation workflow that focuses on how teams verify APIs
as part of documentation maintenance and emphasizes the practice of
testing rather than a specific tool; Core Concepts covers what APIs are and
API testing is about what teams do with APIs, not a fundamental API
characteristic
API docs testing vs QA testing
Both testing approaches are necessary and complementary - QA ensures the product works correctly, while documentation testing ensures that user content is accurate:
| Aspect | QA Testing | Documentation Testing |
|---|---|---|
| What it Tests | APIs meet engineering specifications and function correctly | Documented workflows, code examples, and instructions work as written |
| Source of Truth | Engineering specifications and technical requirements | User-facing documentation and tutorials |
| Purpose | Validates product works to spec | Validates user-facing instructions remain accurate |
| Can catch documentation drift? | No - validates against different source of truth | Yes - specifically designed to catch this |
| Example Scenario | Developers add a required parameter, tests pass → API works correctly | Developers add a required parameter, tests fail → documented examples no longer work |
API docs testing types
| Testing Type | What It Validates | Scope | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contract Testing | API conforms to agreed contracts between consumer and provider | Interface contracts, message formats, protocols | Consumer defines expected response format, provider verifies implementation matches |
| Snippet Testing | Code examples execute successfully | Individual code samples in documentation | Python snippet makes API call and returns expected data structure |
| Workflow Testing | Multi-step API sequences accomplish tasks | Complete user journeys across endpoints | Authentication → create resource → retrieve resource → delete resource all work in sequence |
Example: API docs testing workflow -
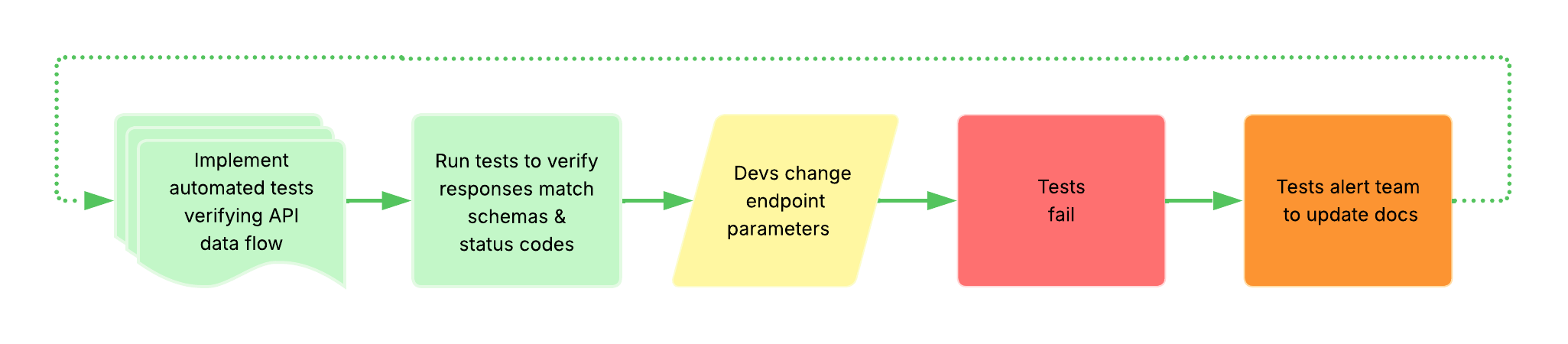
Related Terms: AI agent, API, API sandbox, BDD, Bruno, contract testing, Cypress, Doc Detective, docs-as-tests, HTTP status codes, Playwright, REST API, self-healing system, UX, workflow testing
Sources:
- James Tasse: "Docs as Tests: Part I - On a High (Level)"
- Manny Silva, Docs as Tests: "Validate an API with Doc Detective" by Niko Berry
- Write the Docs Book Club Slack discussions while reading Manny Silva's Docs as Tests, December 2025 - January 2026
BDD
Definition: acronym for behavior-driven development; software development methodology that extends TDD - test-driven development - by writing tests in natural language that describes how software should behave from a user's perspective
Purpose: bridges communication between technical and non-technical stakeholders by expressing requirements and tests in plain language; enables collaboration between developers, testers, and business analysts through shared understanding of expected behavior; in API documentation contexts, allows teams to validate API behavior using human-readable scenarios that serve as both tests and documentation
Example: a team uses BDD to document and test their payment API by writing scenarios that become executable tests through frameworks like Cucumber while simultaneously serving as readable documentation of API behavior -
"Given a valid credit card,
When a charge request is submitted,
Then the transaction succeeds and returns a confirmation ID"
Related Terms: API documentation testing, Cucumber, Given-When-Then, docs-as-tests, workflow testing
Sources:
- Cucumber: "Behaviour-Driven Development"
- Silva, Manny. Docs As Tests. First edition, Release 2, Boffin Education, May 2025.
- Wikipedia: "Behavior-driven development"
contract testing
Definition: verifies APIs and services conform to agreed-upon contracts between consumers/client and providers/server by validating message formats, protocols, and behaviors
Purpose: verifies that the API does what the docs say it does; catches integration issues early without requiring full end-to-end testing environments; ensures API changes don't break existing consumers; specifically ensures that the API definition, implementation, and consumer's code all remain accurate and trustworthy
contract testing vs linters
contract testing validates runtime behavior against executable specifications by testing actual API responses, while linters like Vale perform static analysis of API description documents to check formatting, style, and specification compliance without making requests
Example: consumer team writes tests defining expected API responses, provider team verifies their API implementation satisfies these expectations, catching breaking changes before deployment
Related Terms: API documentation testing, Bruno, docs-as-tests, Dredd, Microcks, Pact, Spectral, snippet testing, Vale, workflow testing
Sources:
- Silva, Manny. Docs As Tests. First edition, Release 2, Boffin Education, May 2025.
- SmartBear Software, Swagger: "What is contract testing and why should I try it?" by Matt Fellows
Critical Chain Project Management
Definition: also known as CCPM; takes the critical path method one step further - focuses on resources needed to complete tasks rather than solely on task dependencies
Purpose: ensures project schedules account for resource constraints, not just task dependencies
Related Terms: Agile, Critical Path Method, project management methodology
Sources:
- UW API Docs: Module 2, Lesson 3, "Introduction to Project Scheduling"
- Wrike: "Project Management Methodologies" by Artem Gurnov
Critical Path Method
Definition: also known as CPM; project management technique identifying task sequences where some tasks can't start until previous ones finish, often visualized with Gantt charts
Purpose: helps teams understand task dependencies and identify bottlenecks in project timelines
Example: the "critical path" in a software release might include the following steps, where delays in any step delay the entire release -
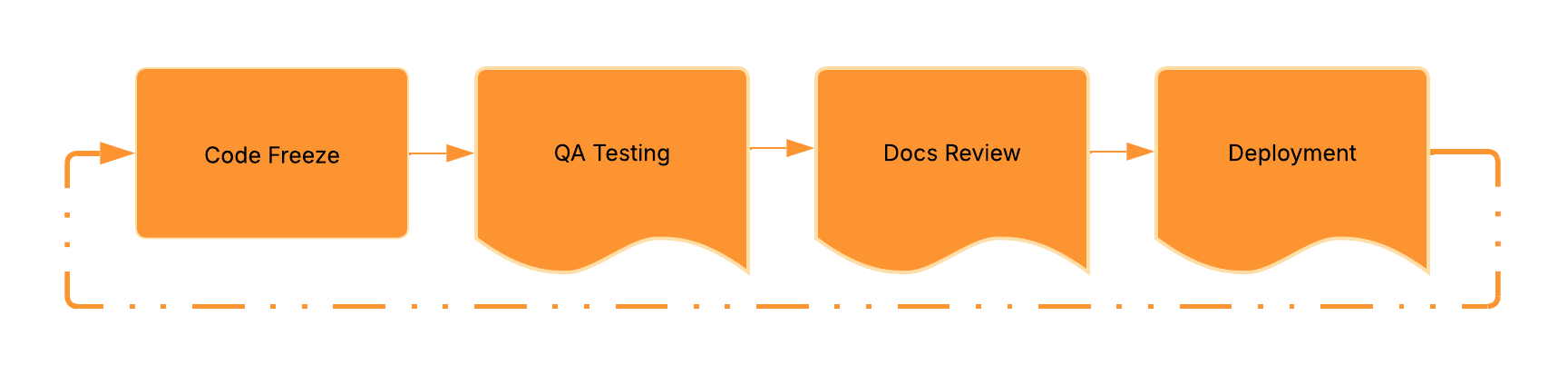
Related Terms: Agile, Critical Chain Project Management, project management methodology
Sources:
- ProjectManager: "A Gantt Chart Guide with Definitions & Examples"
- UW API Docs - Module 2, Lesson 3, "Introduction to Project Scheduling"
- Wrike: "Project Management Methodologies" by Artem Gurnov
diagrams-as-code
Definition: documentation approach that represents diagrams as text-based code artifacts rather than binary image files; subset of the broader docs-as-code philosophy applied specifically to visual information in text form and/or content
Purpose: enables diagrams to live alongside code in repositories, reviewed and maintained through the same workflows as the documentation they support
Why this belongs in Workflows & Methodologies: describes a documentation
methodology and workflow pattern rather than a specific tool; similar to how
docs-as-code describes a tool-agnostic path, diagrams-as-code describes a
capability implemented by tools like Mermaid, PlantUML, D2, and Python Diagrams -
the methodology is distinct from any individual implementation
Example: instead of exporting a PNG from a GUI tool and committing the binary file, a team writes Mermaid or PlantUML markup that renders automatically in their docs platform - when the architecture changes, they update the text, not the image
Key Benefits:
| Benefit | Diagrams-as-Code | Binary Image Files |
|---|---|---|
| Version Control | Text diffs show exactly what connection, label, or component changed; supports inline PR comments | Visual diff shows something changed but not what or why |
| Collaboration | Reviewers comment on specific code lines in PRs | Reviewers describe changes in prose comments |
| Consistency | Tooling handles layout and styling automatically | Manual adjustment required each update |
| Maintainability | Searchable, refactorable, grep-able text | Binary file requires opening a GUI tool to inspect or edit |
| Accessibility | Text source readable by screen readers and LLMs natively | Requires alt text added separately |
Related Terms: accessibility, D2, diagram, docs-as-code, GUI, Ilograph, Large Language Model, Mermaid, PlantUML, pull request, Python Diagrams, UML, version control
Sources:
- DEV Community: "Diagram-as-Code: Creating Dynamic and Interactive Documentation for Visual Content" by Romina Elena Mendez Escobar
- Perforce Software Inc., Gliffy: "Understanding Diagrams as Code From Idea to Implementation"
docs-as-code
Definition: methodology for developing and publishing documentation using the same tools, processes, and workflows as software development
Purpose: enables documentation teams to manage content in version control systems alongside code, leverage developer workflows like pull requests and code review, and automate publishing through CI/CD pipelines; treats documentation files as code artifacts that follow the same quality standards, testing processes, and deployment procedures as software
Why this belongs in Workflows & Methodologies: docs-as-code is
fundamentally a methodology for organizing work, not a specific tool or
analytical framework; it describes a strategic approach to documentation
processes and operational workflows, how teams organize daily documentation
work within development cycles, rather than an evaluation framework like
cognitive dimensions, or a specific software platform, like
Git
or Swagger
Example docs-as-code workflow:
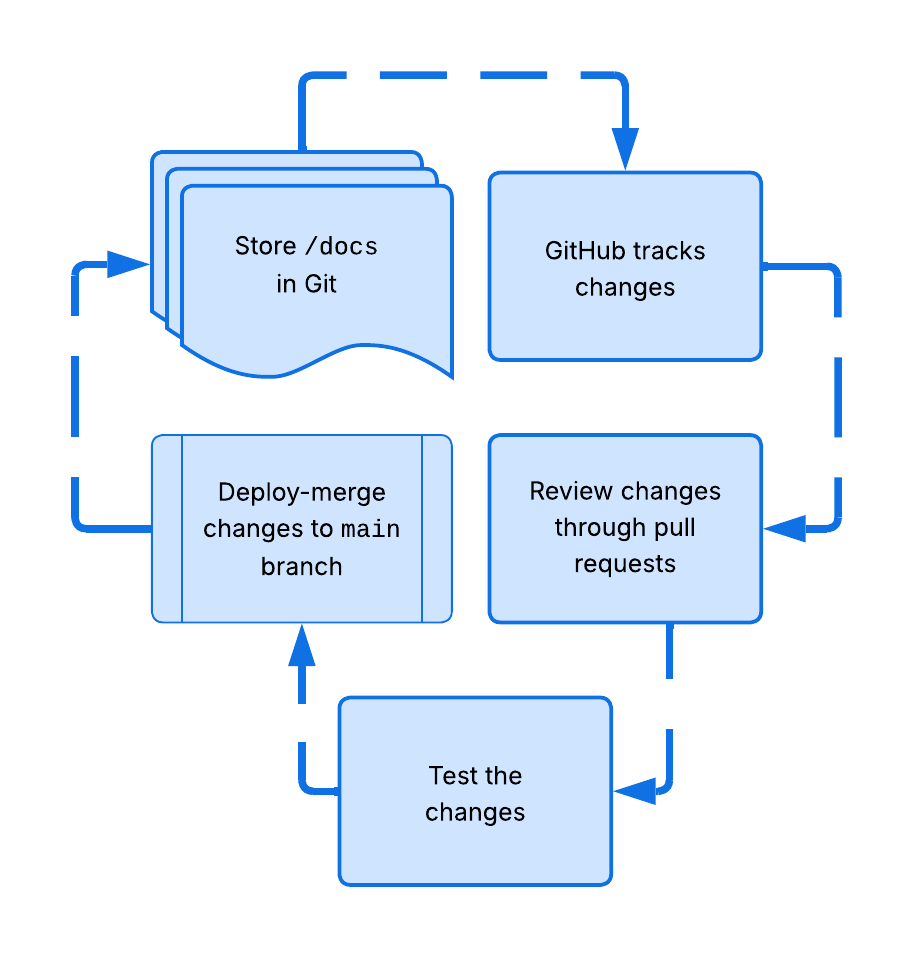
| Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Transparency — all discussions, decisions, and changes visible in one place | Learning Curve - requires all contributors to learn the version control system and toolchain |
| Collaboration — developers draft, writers refine, everyone contributes | Formality - may limit spontaneous collaboration if team relies solely on formal issue tracking |
| Traceability — complete history of what changed and why, accessible years later | Process Dependency - effectiveness depends on comprehensive testing and review processes |
| Efficiency — eliminates context-switching, reduces time searching email or chat | Comm Standards - demands clear communication standards for asynchronous, distributed teams |
| Integration — documentation stays synchronized with code through the same review process | Standardization Balance - success requires balancing standardization with space for informal discussion |
Related Terms: Agile,
CMS,
diagrams-as-code,
docs-as-ecosystem,
Git,
GitHub,
main branch,
MDX,
pull request,
self-healing system,
version control
Sources:
- GitLab: "Five fast facts about docs as code at GitLab"
- UW API Docs: Module 3, Lesson 1, "Introduction to Docs-as-Code"
docs-as-tests
Definition: documentation strategy that treats documentation as testable assertions to verify content accuracy against the current product state
Purpose: maintains documentation accuracy through automated testing that validates docs work as written by directly testing against product UIs, APIs, and CLIs; catches documentation and product issues before users encounter them while reducing manual maintenance effort in environments with frequent product updates; enables technical writers to identify breaking changes in products before release, like how developers use automated tests to catch code regressions
Why this belongs in Workflows & Methodologies: describes an
operational workflow approach that focuses on processes and practices
rather than specific tools or conceptual frameworks
Example docs-as-tests workflow:
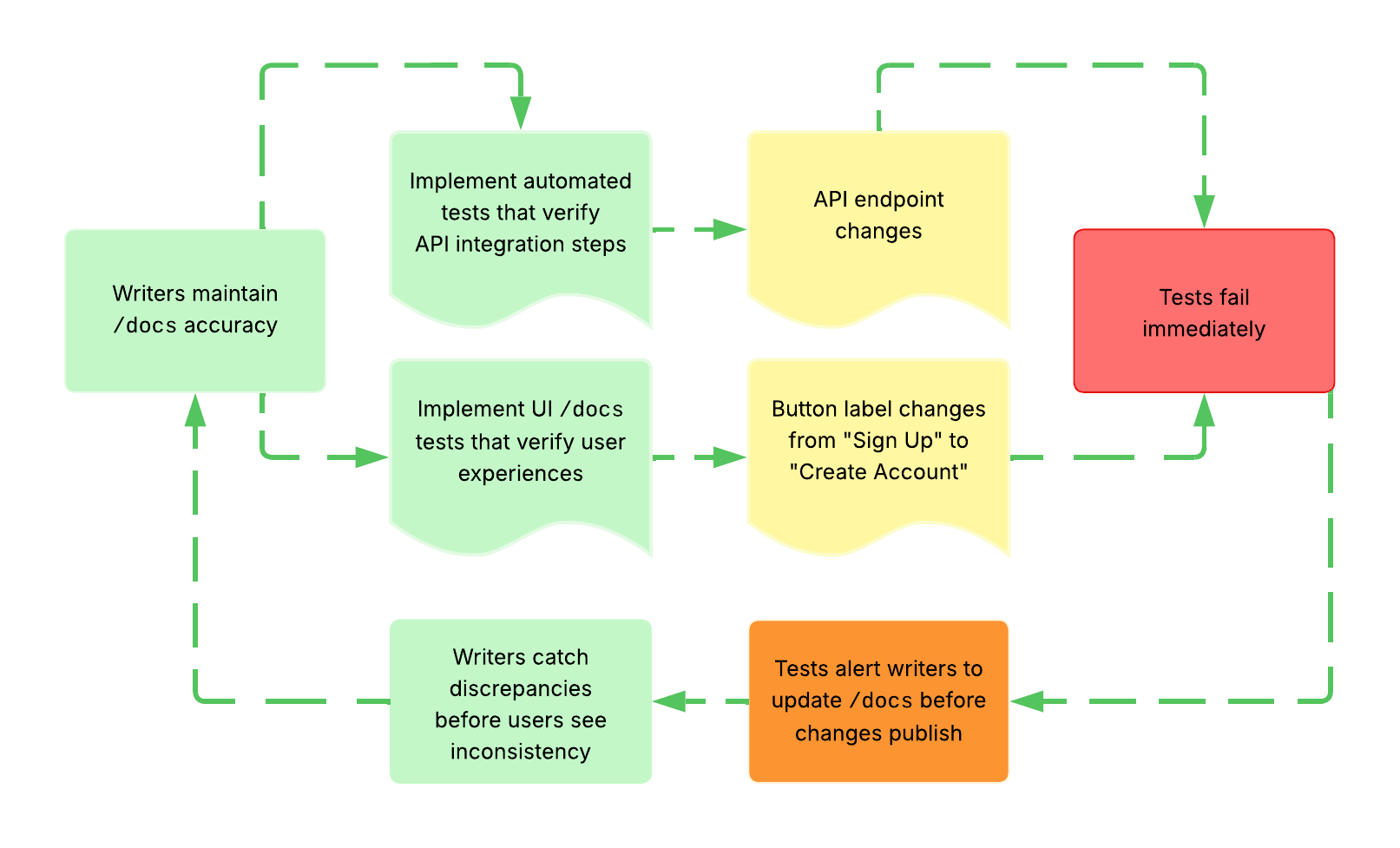
Related Terms: AI agent, API documentation testing, BDD, contract testing, Doc Detective, self-healing system, snippet testing, usability testing, workflow testing
Sources:
- Boffin Education: "About Docs as Tests" by Manny Silva
- James Tasse: "Docs as Tests: Part I - On a High Level"
- Manny Silva, Docs as Tests: "Never have stale docs again"
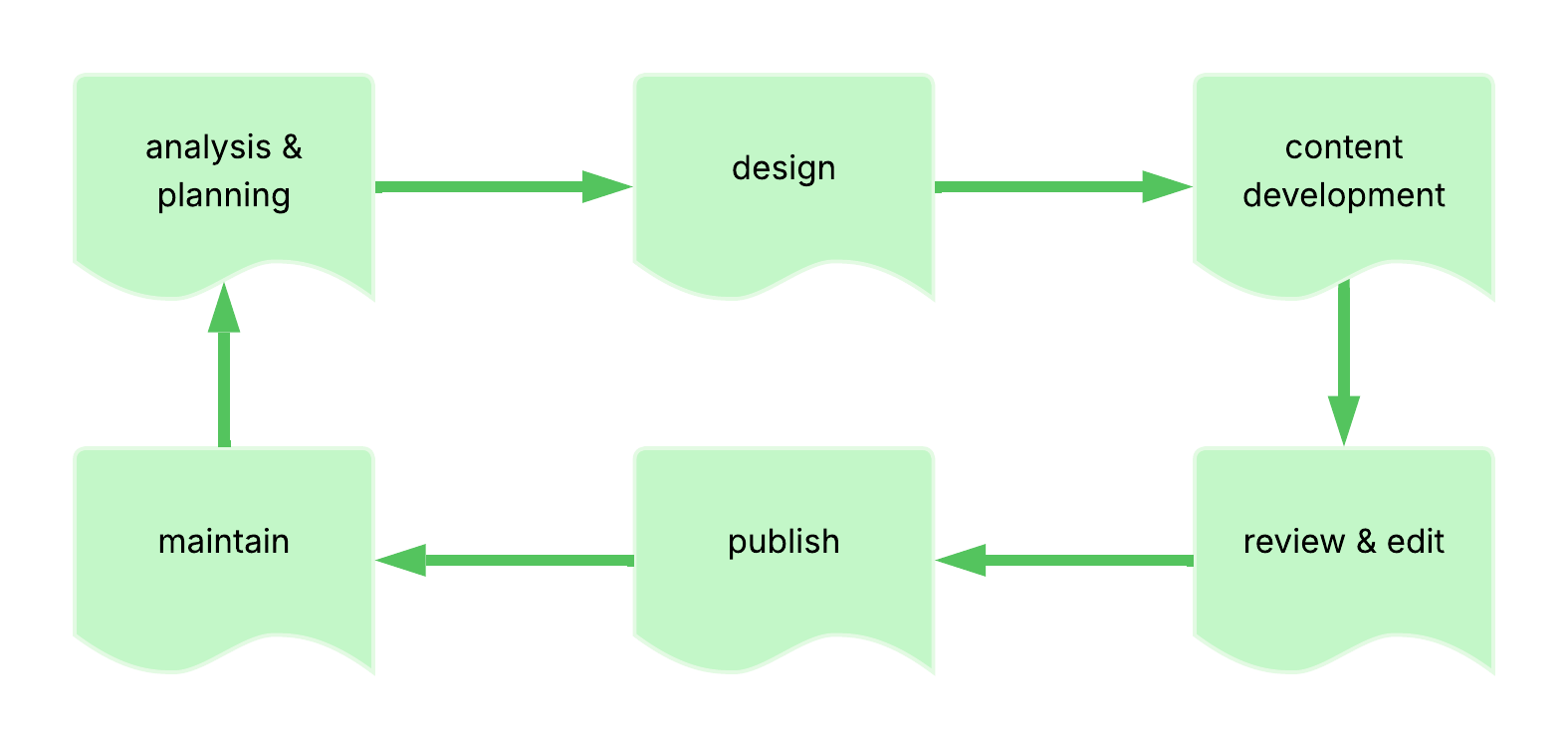
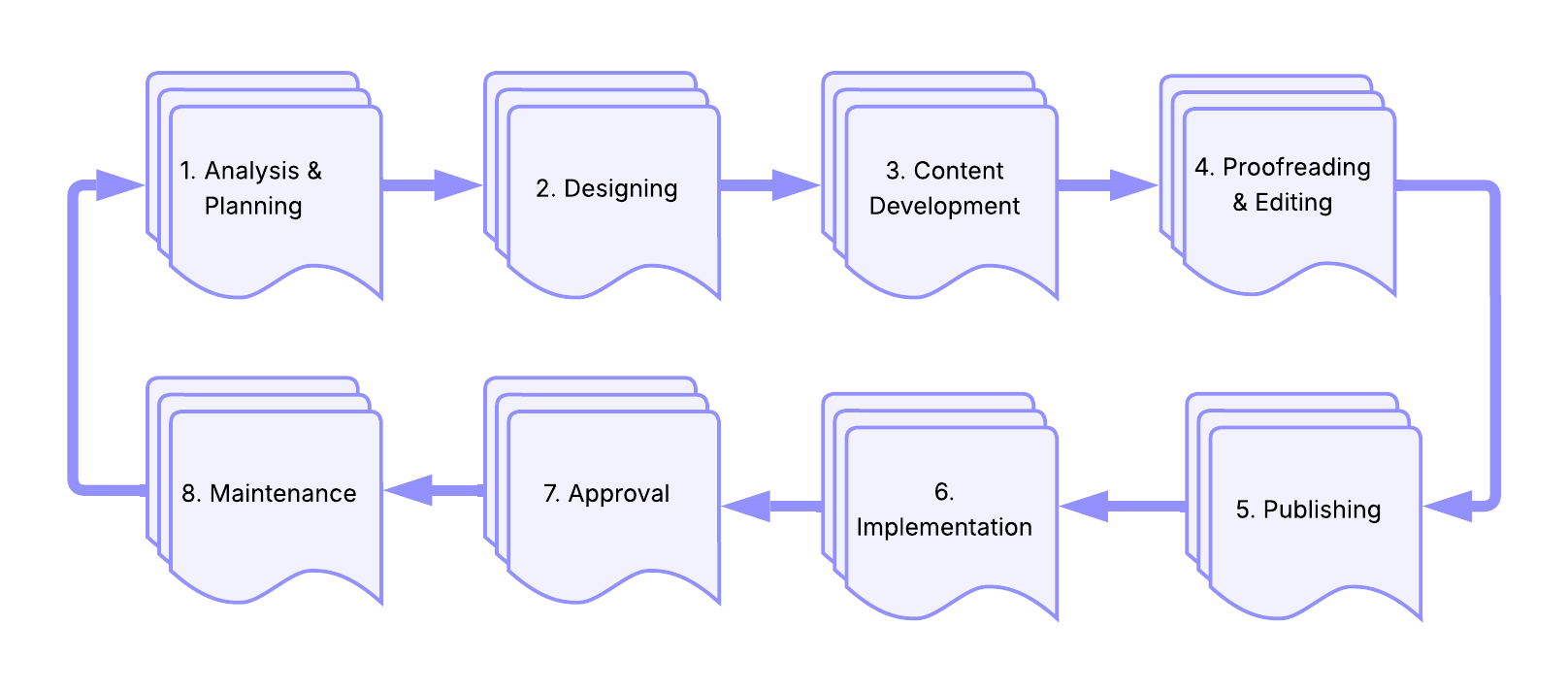
Document Development Life Cycle
Definition: also known as DDLC; process of writing and delivering content in the form of documentation such as PDFs, Word documents, online articles, or website content
Purpose: provides a structured approach to creating documentation with well-defined phases that ensure content meets user needs
Phases:
Related Terms: Agile, API documentation testing, CI/CD pipeline, project management methodology, usability testing
Sources:
- Geeks for Geeks: "Document Development Life Cycle"
- UW API Docs: Module 2, Lesson 3, "Introduction to Project Scheduling"
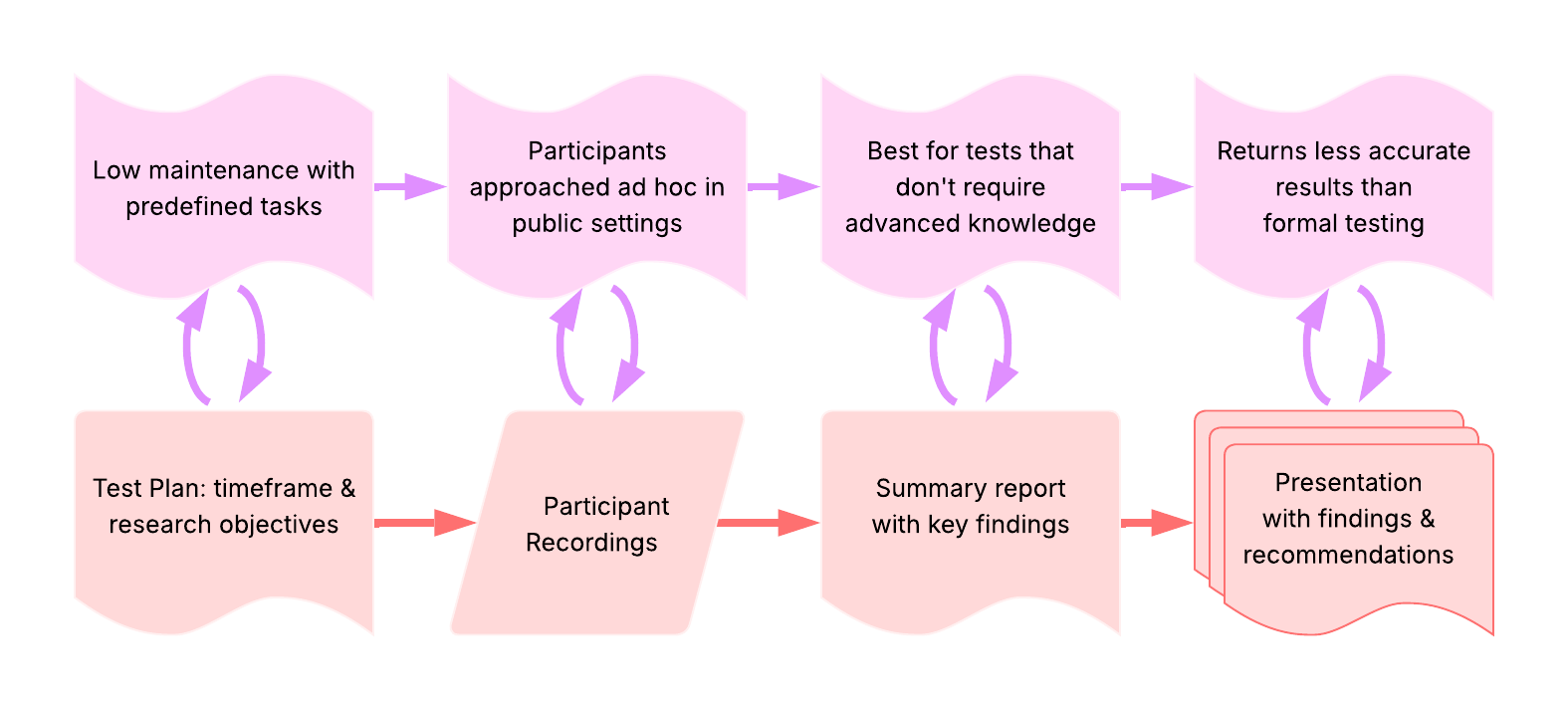
guerrilla usability testing
Definition: evaluation method that tests interface effectiveness by approaching participants in public spaces for quick feedback rather than recruiting in advance
Purpose: provides a quick, cost-effective way to gather feedback from target users without formal recruitment processes
Example: key characteristics and deliverables -
Related Terms: accessibility, AI-assisted usability analysis, API documentation testing, contract testing, Document Development Life Cycle, DX, information architecture, snippet testing, usability testing, UX, workflow testing
Sources:
- Usability Geek: "Guerrilla Usability Testing: How To Introduce It In Your Next UX Project" by Emily Grace Adiseshiah
- UW API Docs: Module 4, Lesson 3, "Review usability testing for API"
project management methodology
Definition: different approaches to organizing and executing projects, ranging from sequential to iterative frameworks
Purpose: provides structured ways to plan, execute, and complete projects based on team needs and project characteristics
common methodologies
| Methodology | Approach | Focus | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waterfall | Sequential, linear | Phase completion | Stable requirements, predictable projects |
| Critical Path Method | Dependency-based | Task sequences | Projects with clear dependencies |
| Critical Chain Project Management | Resource-focused | Resource availability | Resource-constrained projects |
| Agile | Iterative, flexible | Adaptation | Changing requirements, feedback loops |
| Scrum | Sprint-based | Team collaboration | Fast-paced development, quick iterations |
Related Terms: Agile, Critical Chain Project Management, Critical Path Method, Document Development Life Cycle, Scrum, Waterfall
Sources:
- UW API Docs: Module 2, Lesson 3, "Introduction to Project Scheduling"
- Wrike: "Project Management Methodologies" by Artem Gurnov
Scrum
Definition: Agile framework where small teams led by a scrum master work in short two-week cycles called sprints with daily meetings
Purpose: enables rapid development and testing while removing obstacles to efficient work
Example: key characteristics -
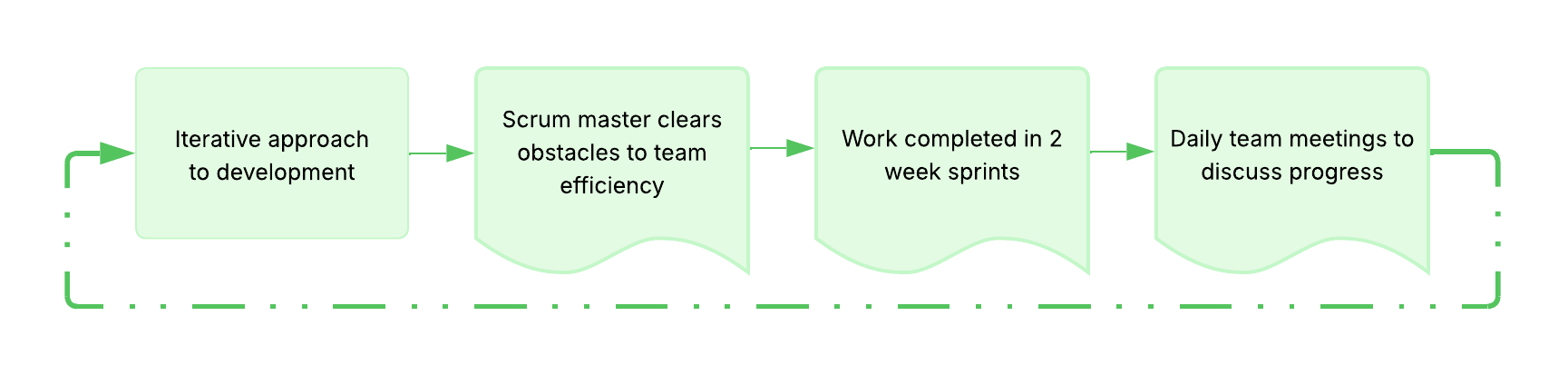
Related Terms: Agile, project management methodology
Sources:
- UW API Docs: Module 2, Lesson 3, "Introduction to Project Scheduling"
- Wrike: "Project Management Methodologies" by Artem Gurnov
snippet testing
Definition: automated testing practice that validates code examples or "code snippets" in documentation execute successfully and produce expected results
Purpose: prevents documentation drift by ensuring code examples remain accurate as APIs evolve; catches breaking changes that would make documented examples fail
Example: documentation builds execute Python code examples against test API instances, failing the build if examples return errors or unexpected responses
Related Terms: API documentation testing, contract testing, docs-as-tests, usability testing, workflow testing
Source: Silva, Manny. Docs As Tests. First edition, Release 2, Boffin Education, May 2025.
usability testing
Definition: practice of testing how easy a design is to use with representative users, typically by observing them as they attempt to complete tasks
Purpose: identifies problems before customers encounter them and provides user perspective before product release
Benefits:
- Finds problems before customers do
- Provides customer perspective pre-release
- Informs design improvements
Limitations:
- Not designed to generalize beyond test scope
- Can't prove that a feature works universally
- Not statistically significant but still useful
- Participant recruitment is challenging
Related Terms: accessibility, AI-assisted usability analysis, API documentation testing, docs-as-ecosystem, Document Development Life Cycle, DX, guerrilla usability testing, information architecture, UX, workflow testing
Source: UW API Docs: Module 4, Lesson 3, "Review usability testing for API"
Waterfall
Definition: traditional, sequential, linear project management methodology where each phase must complete before the next begins
Purpose: provides idealistic approach for projects with well-defined requirements and minimal expected changes
Characteristics:
- Sequential, non-iterative phases
- First introduced by Winston W. Royce in 1970
- Each phase gates the next
- Limited flexibility for changes
Related Terms: Agile, project management methodology, Scrum
Sources:
- Geeks for Geeks: "Waterfall Model - Software Engineering"
- UW API Docs: Module 2, Lesson 3, "Introduction to Project Scheduling"
- Wrike: "Project Management Methodologies" by Artem Gurnov
workflow testing
Definition: validates the sequences of API calls that accomplish real tasks - multi-step interactions and user journeys across multiple endpoints and operations
Purpose: ensures complete business processes work correctly beyond individual endpoint testing; verifies APIs support real-world use cases and user workflows; specifically validates that a series of API calls work together as defined, confirming that users can successfully complete tasks by following documentation procedures
Example: e-commerce workflow test validates entire checkout process by testing user authentication, cart management, payment processing, and order confirmation endpoints in sequence
Related Terms: API documentation testing, BDD, contract testing, docs-as-tests, guerilla usability testing, Karate, snippet testing, usability testing
Sources:
- Silva, Manny. Docs As Tests. First edition, Release 2, Boffin Education, May 2025.
- Testsigma Technologies Inc., Automation Testing: "Workflow Testing | What it is & How to Perform?" by Ranjana Kodlekere